中研院資訊所 IVC Lab 由陳祝嵩教授領導,目前執行科技部AI專案計畫「異質性深度模型整合與檢索特徵學習」。研究主題包含兩個方向:
—深度學習—
含模型壓縮與簡化、深度模型整合、深度永續終身學習、強化學習環境探索、醫療大數據分析、整合影像與聲音的身份辨認等。
—電腦視覺—
含影像與視訊中的物體偵測、人物偵測(人臉、衣著),情緒辨認、美感判讀、空拍機影像偵測、瑕疵檢測、圖像修復、影像序列 3D 建模、醫學影像分析、及大型影像庫快速檢索等。
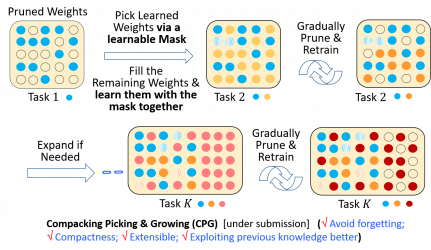
永續終身深度學習(continual lifelong deep learning)-改進資料遺忘及模型擴增度,提昇準確率
#more_013 {display: none;}
監督式深度學習的進展,除了利用已蒐集完成的資料集來進行學習外,也面對另一個困難 ─ 資料並非一次性即可蒐集與建構完成,而是分批獲得;而學習的任務或技能也並非一次可達成,而是在過去以某些資料集學習完相對應任務後,接著再以新的資料集學習新的任務。因此永續性 (continuous) 或終身 (life-long) 學習變得益加重要... 。這部分的方法最大的困難是如何避免災難性地遺忘了過去已習得的任務與技能。我們發展了濃縮化 (shrink) 與擴張化 (expand) 的交替步驟,能夠在避免任務遺忘的情況下,發展出實現多工任務的緊緻模型。並先在tensorflow上進行程式開發與實作,將其運用在持續性學習多個人臉相關任務(身份識別、表情辨認,性別與年齡等),可達成在學習新任務的同時,持續完整地保有舊任務的功能。我們方法的特色是可完全避免遺忘,並在維持深度模型緊緻性 (compactness) 的狀況下來進行擴充。此部分的成果已撰寫論文投稿,並獲得 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR 2019) 所接受。接著我們改良此方法,在壓縮 (compacting) 與 擴張 (growing) 的交替步驟外,另增選擇 (picking) 的步驟,以便類似人類一般在鞏固過去知識的同時,也能藉由選擇過去的關鍵知識來對於目前要學習的新任務有所助益。我們使用可微分的選擇遮罩 (selection mask) 連同模型的保留或擴充權重同時訓練,達成學習新任務但不遺忘舊任務的效果,並以pytorch開發新的技術。此為世界首見同時具有以下特性之技術:不遺忘已學過的任務;保留模型緊湊性;可以無限制增加新任務。成果將發表於AI領域頂尖國際會議 Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019)。
function myFunction_013() { var dots_cpg = document.getElementById("dots_013"); var moreText_cpg = document.getElementById("more_013"); var btnText_cpg = document.getElementById("myBtn_013"); if (dots_cpg.style.display === "none") { dots_cpg.style.display = "inline"; btnText_cpg.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText_cpg.style.display = "none"; } else { dots_cpg.style.display = "none"; btnText_cpg.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText_cpg.style.display = "inline"; } }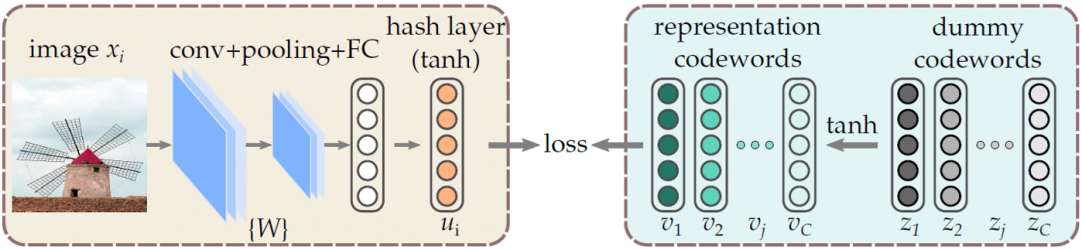
快速檢索碼之深度學習
#more_012 {display: none;}
我們發展無監督與半監督式的二元檢索碼的深度學習技術,以利於在大型資料庫中的快速搜尋與檢索。在半監督式學習中,只有部分的資料被標註,因此以標註的資料為基礎,透過自我學習的方式逐步擴充至未標註的資料,進而達成完整的學習。我們的方法考慮類別之間的關連性,因此類別的 0-1 標籤值也是變數中的一環,可在學習網路權重的同時一同被調整... 。由於我們的方法可以在學習的過程中發掘出類別的相關性,因此更容易將具標籤資料的學習結果推展給無標籤資料使用。目前已經完成初步成果,成果已撰寫論文投稿,並獲得 CVPR 2019 Workshop on Compact Feature Representation and Learning 以及 International Conference on Image Processing 2019 所接受。無監督二元檢索碼的深度學習技術發表於AI領域頂尖期刊 IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2019。其影響因子 (IF: 17.73) 為目前AI領域最高。
function myFunction_012() { var dots_cpg = document.getElementById("dots_012"); var moreText_cpg = document.getElementById("more_012"); var btnText_cpg = document.getElementById("myBtn_012"); if (dots_cpg.style.display === "none") { dots_cpg.style.display = "inline"; btnText_cpg.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText_cpg.style.display = "none"; } else { dots_cpg.style.display = "none"; btnText_cpg.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText_cpg.style.display = "inline"; } }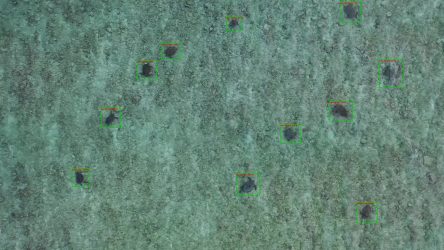
空拍海洋生物辨認整合
#more_011 {display: none;}
本計畫與中山大學機電系劉耿豪及海洋科學系宋克義教授合作,以AI技術之物體偵測方法結合生成式模型方法,實現空拍機東沙群島海面影像之自動游行生物偵測,以節省生物學家所耗費的大量目測統計時間。過去已經完成魟魚偵測之技術開發。今年將進一步發揮本計畫所研發之深度學習模型整合技術之優勢,擴充至同時偵測更多的種類,以期為東沙群島國土保育有所貢獻... 。目前以海龜偵測與追蹤為主。已完成新增種類資料整理標註,並達成不同物種訓練好的之深度偵測模型整合。將於2019年12月份「AI嘉年華」科普活動中提供展示,讓民眾瞭解AI深度學習在環境保育的應用。
function myFunction_011() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_011"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_011"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_011"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
IVCLAB Face Application System
Face Identification & Verification Application

開發整合物體、人臉、及衣著偵測之深度模型,達成進化式的AI辨認功能
#more_010 {display: none;}
為了實現強人工智慧之系統,應用上需要整合各種功能,例如物體偵測、人臉偵測、衣著偵測與人臉辦識。以往的傳統作法中,各自有各自的深度模型,分別獨立訓練與執行。為了讓系統更實用,我們開發統一的深度模型,使用單一的架構來提取特徵,並加上目前的快速偵測框架 Single Shot Detector (SSD),以同時實現四種功能,此部分與新視域科技合作。已經開發包括人臉、物體... 、與衣著偵測之功能。透過我們開發的拉鍊式深度模型整合方法,進行SSD中之骨架 (backbone) 模型的共壓縮整合,將不同任務的偵測與辨認模型成功地整合成單一且多功能的高效模型,打造前所未有的四合一深度辨認模型系統。
function myFunction_010() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_010"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_010"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_010"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }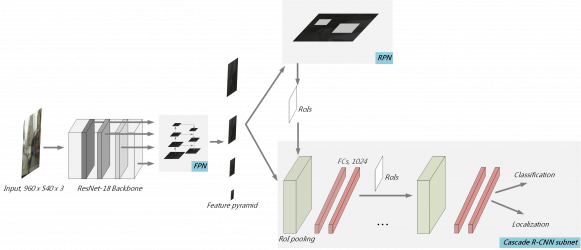
嵌入式平台之車輛與行人影像偵測深度模型開發
#more_014 {display: none;}
我們參與國際多媒體會議IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing(MMSP219)所舉辦的競賽(Embedded Deep Learning Object Detection Model Competition),此競賽任務是,透過行車記錄器影像,設計出偵測車輛與行人之模型,並運行在嵌入式平台(NVIDIA Jetson TX2),在有限的運算資源下,能滿足輕量化、低耗能的需求,並達到一定的準確度... 。我們以Cascade RCNN with FPN(feature pyramid networks)當作初始模型進行改進。針對提升模型準確度,我們提出三個方法。1.對於訓練資料集的連續幀影像,使用間隔數幀採樣,去除冗餘重複的影像,並增加訓練批次(mini-batch)樣本的多樣性。2.針對白天和夜晚車輛有不同外觀的問題,我們把白天和夜晚的車輛分成兩個獨立類別(白天車輛、晚上車輛)訓練,而當要推論(inference)時,則把這兩個類別合併成原本單一類別(車輛)計算準確度,此方法在訓練模型時,能讓模型學習到更好的車輛特徵。3.使用外部資料集增加訓練樣本的豐富性。另一方面,我們針對降低模型的複雜度,提出兩個設計,1.使用輕量化的骨架 (backbone) 模型(ResNet-18),降低模型容量和運算複雜度。2.縮小輸入的影像的尺寸,減少運算複雜度。最終競賽結果,在競賽隊伍中,我們提出的模型擁有最小的模型容量,並且受邀發表論文。相關論文發表於MMSP 2019。
function myFunction_014() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_014"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_014"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_014"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }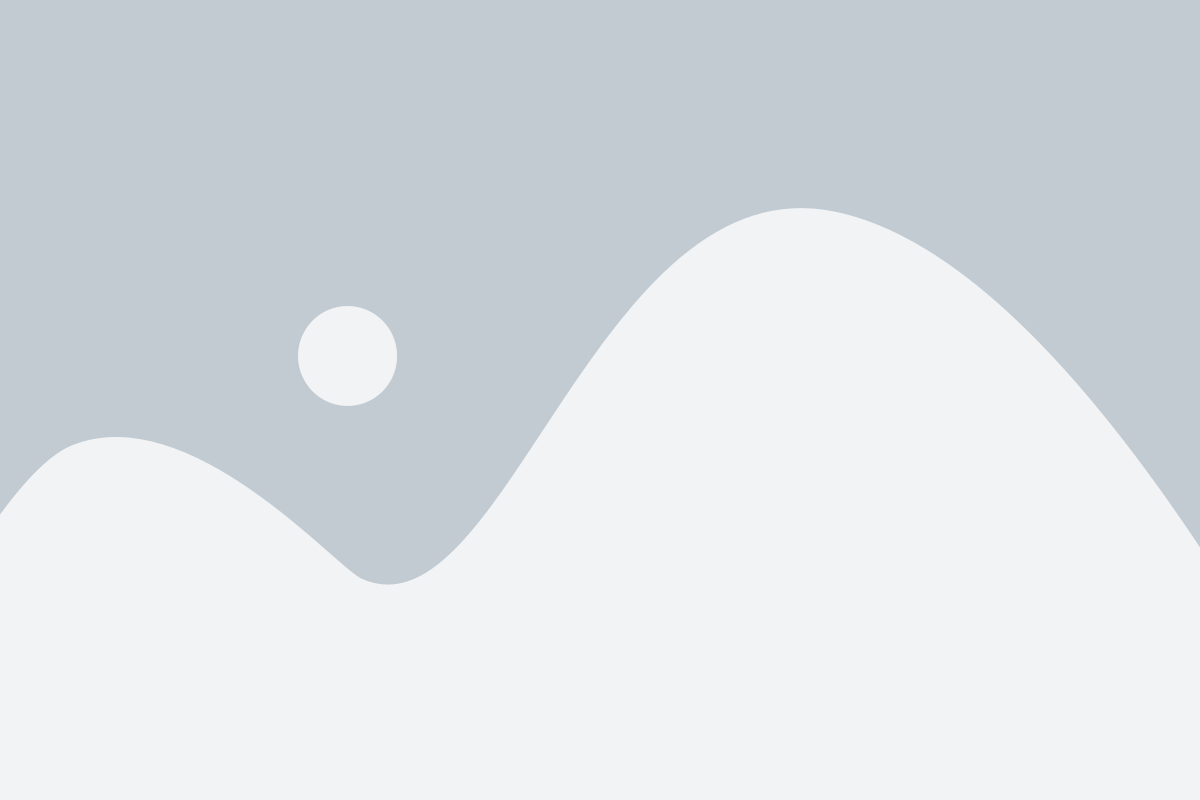
拉鍊式 (zippering) 的深度模型整合方法
#more_009 {display: none;}
當整合架構一致而任務不同的深度模型時,這些任務的資料流在深度模型的運算中有可能維持一致。相較於相異模型整合而言,不同任務間於執行階段有可能共享每層的輸入與輸出,因此無須配置額外的資源來執行不同的任務;故除了能夠達成模型壓縮與推論加速外,亦能實現執行端的記憶體縮減與減少耗能。我們完成拉鍊式 (zippering) 的深度模型整合方法,可以得到一系列的整合模型... 供選用,將兩個不同任務的 MobileNets 整合成為單一的模型,利於佈建已經訓練的 MobileNets 在推論端的裝置,並在執行資源與精準率上達成平衡。相關論文發表於 IEEE HPCA Workshop on Energy Efficient Machine Learning and Cognitive Computing for Embedded Applications, 2019。我們並將所開發拉鍊式 (zippering) 的深度模型整合原理推廣至「同架構不同任務之深度模型整合」。進一步藉由 convolution kernels 可重排後對齊的機制,發展可以整合一般相同型態CNN模型的方法,以增快推論速度與節省執行階段之記憶體需求,對於增進深度學習模型執行效率減少耗能有所助益。可以得到一系列的整合模型供選用。並更進一步藉由 convolution kernels 可重排後對齊的機制,發展可以整合一般相同型態CNN模型的方法,達成增快推論速度與節省執行階段之記憶體需求。具備重排後對齊機制的整合方法正透過院方進行先期專利申請中。技術名稱:具備有效率且多功能推論功能之結合妥善訓練深度模型之系統。
function myFunction_009() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_009"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_009"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_009"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }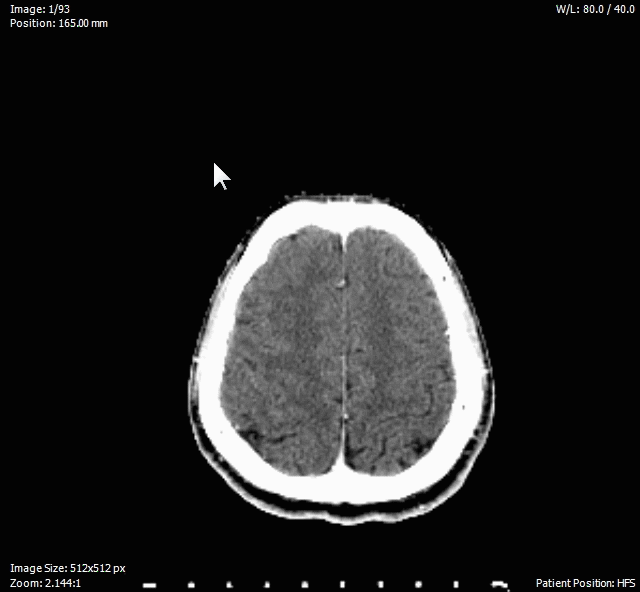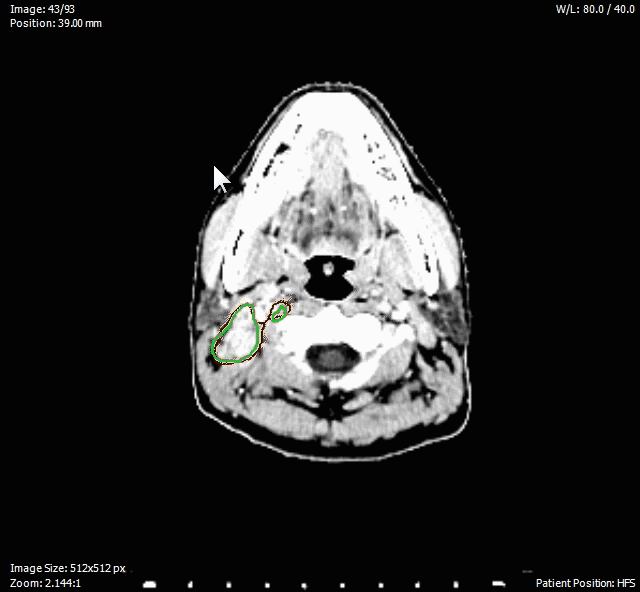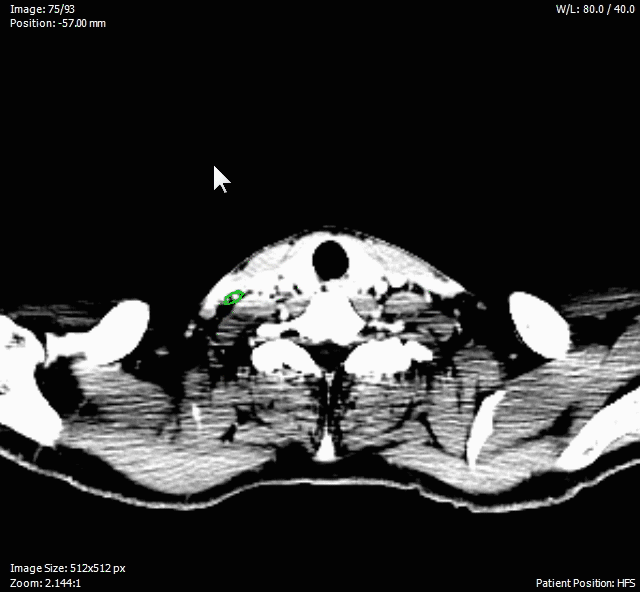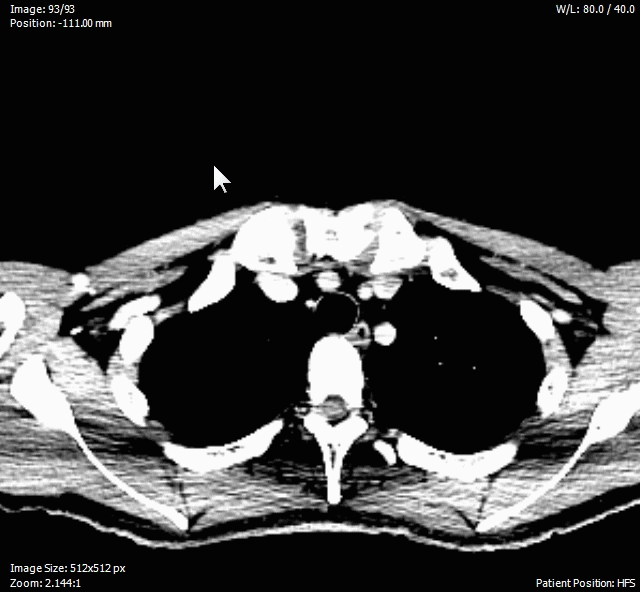
醫學影像鼻咽部腫瘤分割之深度學習模型建置
#more_008 {display: none;}
我們與和信醫院放射腫瘤科合作,以深度學習影像偵測與辨認技術協助癌症檢測,及由影像分析協助放射治療規劃。藉此合作將培養培養團隊人才熟悉醫學影像領域,並將深度模型整合與簡化技術推展到醫學影像處理。去年我們取得了評估影像與進行模型調查與測試。目前AI應用在醫學最有影響力為腫瘤與病灶分割(Tumor and lesion segmentation),而現今解決分割 (segmentation) 問題的深度學習... 網路架構類型為全卷積網路 (Fully convolutional network(FCN)),最具代表性的有U-net跟V-net,以及CascadeAnisotropicCNN。目前學術上雖然有許多團隊針對腦部癌症分割方法,但只有非常少量的資料針對鼻咽部的研究。由於鼻咽部有較多複雜的軟組織,相較於腦部較難處理。我們由和信醫院取得一定量的鼻咽部的影像,考察並測試了相關模型,並對於小區域病灶偵測的效能進行改進。同時我們從事鼻咽部影像深度模型方法之整合與改良,並以強化前處理的方式來提昇準確率,俾便將影像深度整合分析技術應用於不同解析度CT診療流程之改進。
function myFunction_008() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_008"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_008"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_008"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
整合人臉及語者辨認之深度模型技術
#more_007 {display: none;}
我們研發了一個新的方法,可實現已經訓練好之CNN分類網路模型之整合。本法藉由發掘出多個已經訓練後之模型權重值彼此間的相關性,以進行跨模型之統一編碼,俾便達成權重值之壓縮且共用的目的。目前雖有單一深度模型的壓縮與簡化方法,然仍叫缺乏同時兼顧模型權重值之壓縮與共用的方法出現。本法是世界上首見可於推論階段進行深度模型整合之技術,可進行網路共編碼與校正學習... :將不同網路的權重進行對應層之間的共編碼,原本的網路結構因而得以維持;我們並推導出可共編碼後 codebook仍可偏微分 (differentiable)的性質,故可持續利用倒傳遞演算法將共編碼的 codebook 進行校正訓練與優化。我們將其應用於在推論端整合人臉及語者辨認之深度模型,成果被 CVPR 2019 Workshop on Multimodal Learning and Applications 接受為口頭發表論文。
function myFunction_007() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_007"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_007"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_007"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
等價性 CNN 掃描網路理論分析
#more_006 {display: none;}
在深度CNN網路的基礎理論上,本計畫也具有相當不錯的進展。當一個CNN網路模型被建構完成後,我們有時會將之當成一個功能方塊 (building block) 用以掃描更大範圍的影像或訊號,以達到目標偵測或者影像轉換等功能。這樣的掃描過程等同於使用一個大的CNN網路於此大範圍影像。若能找出這個等價的CNN網路,即可避免掃描過程中的重複計算,從而大幅提昇推論效率。我們證明了... 與掃描等價之CNN網路存在的必要條件是原先的功能方塊是由藉由未補邊 (un-padded) 之CNN 所構成;並且藉由訊號處理中的 Nobel Identity 原理的推廣,提出了建構等價 CNN 的作法(圖三),及等價網路與擴張性卷積運算 (dilated convolution) 之間的高度關連性。我們的方法特點是有助於提昇CNN深度網路掃描的運算效率。藉由我們的理論基礎,可建構新一代的CNN影像轉換網路結構。本成果發表於國際知名期刊 IEEE Signal Processing Letters。
function myFunction_006() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_006"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_006"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_006"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }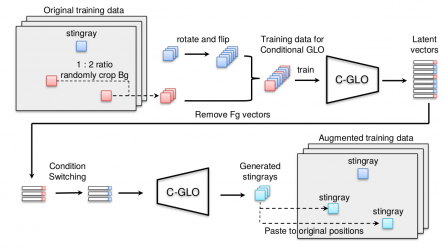
物體偵測 (object detection) 深度模型之資料擴增 (data augmentation) 技術開發與測試:
#more_005 {display: none;}
(1) [技術開發] 在深度學習的訓練中,經常會遇到訓練資料量不足的問題。在分類的深度模型訓練上,一個常用的技巧為資料擴增,也就是以旋轉,翻轉,裁切 (cropping) 等方式來增加訓練資料,從而達到更好的辨認準確率。然而在物體偵測的工作上,不只是要辨認出物體的類別,也要同時框選出物體的所在位置,但是在物體偵測的訓練上仍缺乏有效的資料擴增的技術。為彌補此不足...
,我們發展了一個基於生成器 (generator) 的資料擴增方法,可在已有的影像背景中生成前景的物體,進而擴充前景物體的訓練資料量,以提昇物體偵測準確率(圖四)。我們的方法 (conditional GLO; C-GLO) 毋須像 generated adversarial network (GAN) 般需要額外的判別器 (discriminator) 以從事競爭性訓練,而是可直接藉由降低損失函數的方法來進行生成器的訓練,因此在訓練階段能更加快速與穩定地收斂。訓練好的生成模型藉狀態切換 (condition switch) 之後, 即可在給定的背景影像區塊中生成不同形狀的前景物體,以有效地擴充物體偵測中前景物體的訓練資料。成果發表在ICIP 2018 以及CVPR 2018中專門為海洋視訊分析與環境監測舉辦的研討會。
(2) [海洋生物偵測應用]
我們將 C-GLO 的方法應用在空拍機海面影像之自動游魚偵測,以建構更好的物體偵測網路,節省生物學家所耗費的大量目測統計時間。經由我們研發的資料擴增方法,相對於原本物體偵測網路 faster RCNN,在搭配之骨幹網路 (backbone network) 為ZF-Net下之準確率可提高 5% 以上。未來我們將擴充至更多種類的海洋生物偵測。
深度模型融合:Merge and Compress Well Trained Deep Neural Networks for Mobile Devices
#more_004 {display: none;}
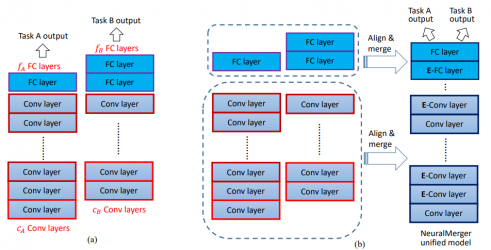
在深度學習方面,隨著各種模型的發展與成熟,一個主要問題是許多訓練好的模型都僅專精某一項特別的任務。基於此,我們研發深度模型整合方法,目標為利用既有已學習好的單一任務網路,將其合併 (merge) 成為單一的多功能網路。我們的方法可以實現已經訓練好之 CNN 分類網路模型之整合 ─ 目前雖已有單一深度模型的壓縮與簡化方法,然仍未有同時兼顧模型權重值之壓縮與共用的方法出現...
。因此本方法是首次於推論端進行深度模型整合之技術。其特點包括了
(1)所整合的CNN模型可具備不同的層數,其卷積核大小與數目也可不盡相同。
(2)將不同網路的權重進行對應層之間的共編碼,原本的網路結構因而得以維持; 並推導出共編碼後的 codebook 仍可偏微分 (differentiable) 的性質,故可持續利用倒傳遞演算法將共編碼的 codebook 進行再訓練與優化。
(3)整合好的模型可作為基礎,繼續整合其它模型,以達成更多功能。目前完成的方法與成果已發表於 AI 領域頂尖國際會議 IJCAI 2018。在整合人臉性別預測及服裝辨認的工作上,經本法整合後之深度模型大小為原本的1/12 (壓縮比),執行速度以 CPU 實測分別快 1.8 與 2.5 倍以上;其平均準確率可幾乎維持相同。
深度回憶:速搜特徵學習 ─ Learning Efficient Deep Representations for Recognition and Retrieval
#more_003 {display: none;}
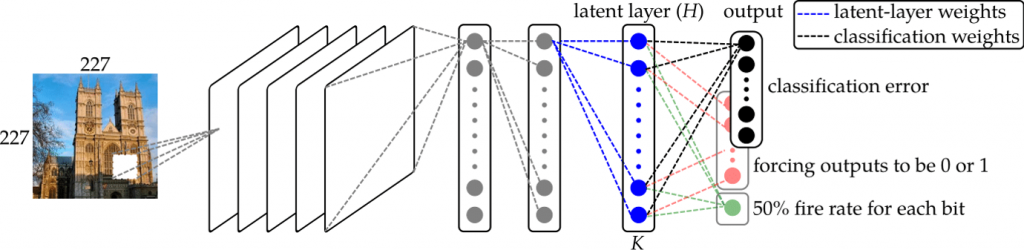
我們發展了世界領先之深度學習二元雜湊編碼技術。在此研究方向中,我們致力於研發以深度學習來建構快速檢索特徵碼之方法,以利於大型資料庫中進行物件搜尋。過去大部分深度學習的方法皆針對分類問題作設計,擅長於標籤判斷,但並不一定適合於相關連例子之間 (relevant instance) 的搜尋與比對。然而檢索所需之空間龐大,經常需要以二元 (binary) 或雜湊 (hash) 碼的方式存取以降低所需空間並增進存取效率...
。在深度學習時代,我們於 2015 年首先提出以潛在層 (latten layer) 為基礎分類網路方法,並以此達成二元特徵碼的監督式學習。此潛在層方法的原理在後來廣泛影響深度學習二元快速特徵碼的設計,許多後續工作都參考我們的方式,以潛在層來進行hash codes 的學習。我們方法的特色是可在不影響分類準確率的方式下,增快檢索速度。優點包括
(1)僅需稍加調整現有的深度學習網路架構即可進行速搜檢索特徵學習、易於實行。
(2)適用於大型資料集的訓練。
(3)可同時兼顧檢索及分類工作。
2016年我們進一步將方法推展至無監督的binary codes學習,發表於電腦視覺國際會議 CVPR 2016。這些方法的完整研究成果亦被機器智慧領域最頂尖期刊 IEEE TPAMI 接受 (impact factor 2017: 9.455; 2018:17.730)。我們發展的方法已經成為國際上深度學習二元特徵碼的代表性方法之一,具有廣泛的影響力。相關技術在google scholar 共被引用達 500 次以上。
"Deep Learning of Binary Hash Codes for Fast Image Retrieval,” CVPRW 2015, 302 times.
"Learning Compact Binary Descriptors with Unsupervised Deep Neural Networks," CVPR 2016, 125 times.
"Supervised Learning of Semantics-Preserving Hash via Deep Convolutional Neural Networks," IEEE TPAMI 2018, 103 times.
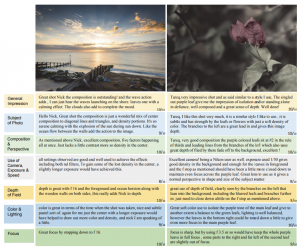
相片美感自動評述─ Computational Aesthetics for Photo Critics
#more_002 {display: none;}
深度學習之多模態整合。結合視覺與自然語言,開發基於美感觀點的影像描述技術。近年來,許多從事於電腦視覺的學者紛紛開始著手研究如何使用電腦計算的方式來進行照片的美學估量 (photo aesthetics assessment)。自動美感評估有多方面的應用,例如相片編輯軟體,搜尋系統等。以電腦計算的方式來進行照片品質的估量不僅對於一般專業攝影師有所助益... ,也具有許多日常生活方面的實用性。舉例來說,一般家庭可以用來進行相片篩選及相簿製作,網站編輯可在短時間內選出高品質的照片來呈現新聞報導,網路相簿或搜尋引擎也可利用此功能去進行相片的分類與展示等。然而一張圖勝過千言萬語,亦即相片可透過不同的角度或觀點來加以詮釋或評述。我們透過 CNN影像辨認並延伸 seq-2-seq 的深度語言編碼/解碼模型,發展出世界首見可為相片自動進行拍攝美感評論 (aesthetic critics) 的方法,成果發表於電腦視覺頂尖國際會議 ICCV2017。可運用於聊天機器人及自動拍攝教學等應用系統上。
function myFunction_002() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_002"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_002"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_002"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
序位學習(及其於人臉年齡估測之應用): Ordinal regression (and Its Application to Age Estimation based on Human Faces)
#more_001 {display: none;}
我們提出新的序位學習 (ordinal ranking) 原理及其理論上界值之分析,以有效提升電腦視覺人臉資訊處理的重要問題─年齡估測的準確性。序位學習問題的特色是其標籤具順序性,過去我們提出拆解成多個二元 (binary) 分類問題再加以整合,可得到比直接回歸或分類更好的年齡估測效果。而如何設定二元分類的代價值是關鍵之一。我們建構出可讓具順序的標籤分類更加準確的代價設定法則...,並進行理論的推導與有效性的證明。其後我們採用 scattering transform,優點是其為卷積網路之架構,然毋須經過學習即可取得人臉特徵表示。我們在此課題的系列成果是解決年齡估測問題的經典方法,已被廣泛引用並具高能見度和影響力,除傳統圖形識別外,亦影響後來深度學習相關課題作法走向。過去在 CVPR 2011 的論文被高度引用,而發表於 IEEE TIP 2015 的期刊論文已經引用達 64 次。如頂尖國際會議CVPR2017 的論文 "Using Ranking-CNN for Age Estimation" 即大量參考本方法,並進一步尋求理論上界分析的改進。CVPR2018 的論文 "Deep Cost-Sensitive and Order-Preserving Feature Learning for Cross-Population Age Estimation" 亦借鏡了許多我們的處理方式,及藉改良 loss function 來提升準確度。整體而言,我們的系列研究開啟了 cost-sensitivity及ordinal ranking 技術在年齡估測上的先河,並帶動了這方面作法在年齡估測課題上之蓬勃進展。
function myFunction_001() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_001"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_001"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_001"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }~ Before 2013 ~

Assessment of Photo Aesthetics with Efficiency
#more_b13_13 {display: none;}
Photo quality assessment has been a popular research topic. Many previous works achieved high classification rates in photo aesthetics assessment by designing new aesthetic features. However, those hand-crafted features sometimes are not describable, or are very time-consuming and thus... not applicable for real-time applications. In this paper, we propose aesthetic features with high efficiency to compute. The experimental results show that our proposed features reach considerable performance. The computation consumption for classifying an image is low so that it is possible to realize online assessment in photo capturing and provide instant feedback to users or fulfill photo rating system on portable devices.
function myFunction_b13_13() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_13"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_13"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_13"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
From Rareness to Compactness: Contrast-Aware Image Saliency Detection
#more_b13_12 {display: none;}
Contrast-Aware Saliency (CAS) to detect visual saliency by utilizing two general characteristics: rareness and compactness. In our approach, multiple-salient-spots are used to find initial salient clues, which appear to be rare and unique parts in an image. Then, the salient regions... are detected by aggregating the surrounding regions of the spots, which fulfil the compactness nature of salient objects. Experimental results show the proposed CAS performs well in the benchmark dataset.
function myFunction_b13_12() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_12"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_12"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_12"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
Affinity Aggregation for Spectral Clustering
#more_b13_11 {display: none;}
We propose affinity aggregation spectral clustering (AASC), a method for aggregating affinity matrices for spectral clustering. AASC can explore strengths of different features automatically and weight them properly. Experiments show that it effectively incorporates multiple affinities and... yields better performance compared to spectral clustering with only a single affinity or naive feature fusion strategies. In addition, AASC is easy to implement, since only the computation of eigenvectors and 1-D search are involved.
function myFunction_b13_11() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_11"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_11"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_11"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
Multiple Kernel Fuzzy Clustering
#more_b13_10 {display: none;}
We here extend the multiple kernel-learning paradigm to fuzzy clustering. The proposed multiple kernel fuzzy c-means (MKFC) algorithm simultaneously finds the best degrees of membership and the optimal kernel weights for a nonnegative combination of a set of kernels. MKFC is... easy to implement and provides soft-clustering results that are immune to irrelevant, redundant, ineffective, and unreliable features or kernels. Experiments show that the method effectively incorporates multiple kernels and yields better overall performance. These characteristics make it useful for real-world applications.
function myFunction_b13_10() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_10"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_10"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_10"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }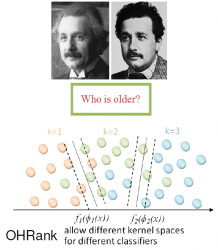
Ordinal Hyperplanes Ranker with Cost Sensitivities for Age Estimation
#more_b13_08 {display: none;}
In this research, we propose an ordinal hyperplane ranking algorithm called OHRank, which estimates human ages via facial images. The design of the algorithm is based on the relative order information among the age labels in a database. Each ordinal hyperplane separates all the facial images... into two groups according to the relative order, and a cost-sensitive property is exploited to find better hyperplanes based on the classification costs. Human ages are inferred by aggregating a set of preferences from the ordinal hyperplanes with their cost sensitivities. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms conventional multiclass-based and regressionbased approaches as well as recently developed rankingbased age estimation approaches.
function myFunction_b13_08() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_08"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_08"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_08"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
A Ranking Approach for Human Age Estimation Based on Face Images
#more_b13_07 {display: none;}
In our daily life, it is much easier to distinguishwhich person is elder between two persons than how old aperson is. When inferring a person’s age, we may compare his or her face with many people whose ages are known, resulting in a series of comparative results, and then we conjecture... the age based on the comparisons. This process involves numerous pairwise preferences information obtained by a series of queries, where each query compares the target person’s face to those faces in a database. In this paper, we propose a ranking-based framework consisting of a set of binary queries. Each query collects a binary-classification-based comparison result. All the query results are then fused to predict the age. Experimental results show that our approach performs better than traditional multi-class-based and regression-based approaches for age estimation.
function myFunction_b13_07() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_07"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_07"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_07"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }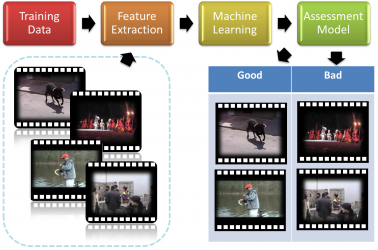
Video Aesthetic Quality Assessment By Combining Semantically Independent and Dependent Features
#more_b13_06 {display: none;}
This research aims to accomplish the work of assessing the aesthetic quality of a video. Unlike previous assessing works focusing mainly on the extraction of aesthetic features in a film, we further study the features, discover their semantic property on videos and then come up... with more useful videobased features such as motion space and motion direction entropy. In the experiment, we compare the assessing accuracy between two different semantic types of features and find that the semantic-independent feature is more reliable from the results. By combining all features, our method learned a more robust and accurate assessment model.
function myFunction_b13_06() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_06"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_06"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_06"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
Multi-Camera Tracking
#more_b13_05 {display: none;}
In this research, we propose an unsupervised method which learns adaptively and can be applied to long-term monitoring. Furthermore, we propose a method that can avoid weak links and discover the true valid links among the entry/exit zones of cameras from the correspondence. Experimental... results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods in learning both the spatio-temporal and the appearance relationship, and can achieve high tracking accuracy in both indoor and outdoor environment.
function myFunction_b13_05() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_05"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_05"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_05"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
Temporal Color Consistency based Video Reproduction for Dichromats
#more_b13_04 {display: none;}
The goal of this research is to reproduce videos to enhance the visibility for color vision deficient viewers and the temporal color consistency has to be guaranteed. Temporal color consistency means the same colors appearing in different frames are re-colored to identical... new colors.
function myFunction_b13_04() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_04"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_04"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_04"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }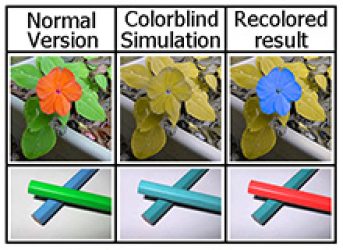
An Efficient Approach to Image Recoloring for Dichromats Based on Priority Order of Colors
#more_b13_03 {display: none;}
People with color vision deficiency (CVD) have difficulty to discriminate certain categories of color combinations. This project aims to repaint images to enhance the accessibility for CVD viewers with naturalness preserving. The property of naturalness preserving is considered to... keep colors that are originally visible by dichromats and only the un-distinguishable colors are modified in the CVD space.

Common Pattern Discovery
#more_b13_02 {display: none;}
Rough face alignments lead to suboptimal performance of face identification systems. In this study, we present a novel approach to identify genders from facial images without proper face alignments. We combine the beneficial properties of linear subspace and discriminative set... classification methods to achieve the goal. The proposed approach with unaligned facial images is shown to outperform the state-of-the-art methods with face alignment.
function myFunction_b13_02() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_02"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_02"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_02"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }
AN ADAPTIVE APPROACH FOR OVERLAPPING PEOPLE TRACKING BASED ON FOREGROUND SILHOUETTES
#more_b13_01 {display: none;}
We propose Binary/Appearance Tracker which consists of background subtraction, silhouette similarity and particle filter to infer the pedestrians’ locations under different occlusion situations with a single camera. During the period of occlusions, binary and color... silhouette likelihoods are adaptively used to effectively measure the similarity between the foreground and the possible combinations of silhouettes. The experimental results show that the proposed BATracker can track people successfully even though she/he is fully occluded.
function myFunction_b13_01() { var dots = document.getElementById("dots_b13_01"); var moreText = document.getElementById("more_b13_01"); var btnText = document.getElementById("myBtn_b13_01"); if (dots.style.display === "none") { dots.style.display = "inline"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read more"; moreText.style.display = "none"; } else { dots.style.display = "none"; btnText.innerHTML = "Read less"; moreText.style.display = "inline"; } }